Unlock Weight Loss: 5 Surprising Gut Health Secrets You Need
For years, the weight loss equation seemed simple: eat less, move more. While calorie balance is undeniably important, science is increasingly showing us that there’s a much deeper, more intricate story unfolding right inside our bodies—specifically, in our gut. The connection between gut health and weight loss is far more profound than most people realize, acting as a hidden lever that can either accelerate your progress or keep you stuck.
Imagine your gut as a bustling city, teeming with trillions of microorganisms—bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. This complex ecosystem, known as your gut microbiome, plays a pivotal role in almost every aspect of your health, from immunity and mood to, yes, your ability to manage your weight. If you’ve been struggling to shed those stubborn pounds despite your best efforts, it might be time to look beyond the calorie count and delve into the fascinating world of your digestive system.
This comprehensive guide will explore the undeniable link between your gut and your weight, revealing how specific bacteria can influence everything from your cravings to your metabolism, and what you can do to cultivate a thriving gut that supports your weight loss goals.
The Gut Microbiome: Your Inner Weight Loss Team
The sheer number of microbes in your gut is astonishing—outnumbering your own cells by a factor of 10 to 1! This isn’t just a random collection; it’s a sophisticated community where different species perform different jobs. When this community is balanced and diverse, it works for you. When it’s out of whack, it can work against your weight loss efforts. This is the core of understanding gut health and weight loss.
- Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: Your gut bacteria help break down food, especially complex carbohydrates and fibers that your body can’t digest on its own. They extract nutrients and create beneficial compounds like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are crucial for energy and gut lining integrity.
- Influencing Metabolism: Certain types of gut bacteria have been shown to influence how your body stores fat, how it responds to insulin (which regulates blood sugar), and even how many calories it extracts from food.
- Regulating Appetite and Cravings: Believe it or not, your gut microbes can communicate with your brain! They produce neurotransmitters and hormones that impact your mood, stress levels, and even your feelings of hunger and fullness. An imbalanced gut might send signals that promote cravings for unhealthy foods.
- Inflammation Control: Chronic low-grade inflammation is often associated with weight gain and difficulty losing weight. A healthy gut microbiome can help keep inflammation in check, while an unhealthy one can promote it.
Gut Bacteria and Metabolism: A Two-Way Street
The interplay between your gut bacteria and metabolism is incredibly intricate. Research has identified key differences in the microbiomes of lean individuals compared to those who are overweight or obese. For instance, two major phyla of bacteria, Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes, are often discussed in this context.
- Firmicutes vs. Bacteroidetes: Studies suggest that individuals with a higher ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes tend to extract more calories from food and store more fat. While not a definitive cause-and-effect, it highlights how the composition of your gut bacteria can impact your metabolic efficiency.
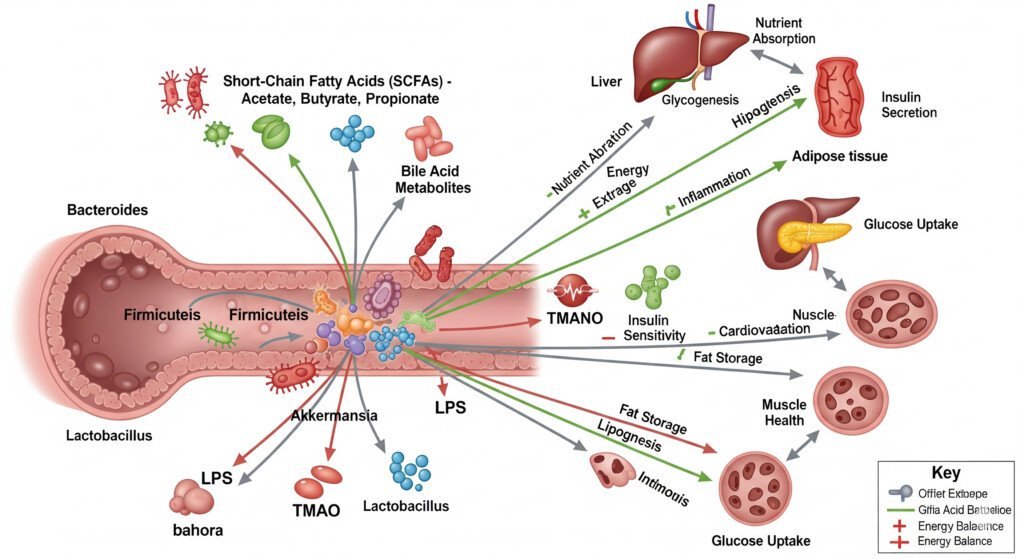
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs): When your gut bacteria ferment dietary fiber, they produce SCFAs like butyrate, propionate, and acetate. Butyrate, for example, is vital for the health of your gut lining and may help regulate metabolism and suppress appetite. Propionate has been linked to reduced food intake.
- Bile Acid Metabolism: Your gut microbes also play a role in metabolizing bile acids, which are crucial for fat digestion and absorption. Altered bile acid profiles can influence fat metabolism and energy expenditure.
In essence, your gut bacteria can dictate how many calories your body absorbs, how efficiently it uses energy, and how it handles fat storage. This profound influence makes gut health and weight loss an inseparable duo.
Probiotics for Fat Loss: Friend or Foe?
The idea of taking probiotics for fat loss has gained immense popularity, but it’s important to approach this with a nuanced understanding. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. Not all probiotics are created equal, and their effects can be strain-specific.
- Specific Strains Matter: While general probiotic supplements can support overall gut health, research suggests that certain strains may have a more direct impact on weight management. For example, Lactobacillus gasseri has shown promise in some studies for reducing abdominal fat. Other strains, like Bifidobacterium lactis, have also been investigated.
- How They Might Help: Probiotics may aid fat loss by:
- Reducing the absorption of dietary fat.
- Altering the balance of gut bacteria to favor beneficial strains.
- Reducing inflammation in the gut and body.
- Improving insulin sensitivity.
- Producing appetite-regulating hormones.
- Not a Magic Bullet: It’s crucial to understand that probiotics are not a substitute for a healthy diet and regular exercise. They are best viewed as a supportive tool to enhance your overall gut health and weight loss strategy, not a standalone solution for shedding pounds. When selecting a probiotic supplement, look for one that specifies the strains and colony-forming units (CFUs) and ideally, choose a diverse blend.
Gut Microbiome Weight Loss: Restoring Balance for Results
So, how do you actively cultivate a gut microbiome for weight loss? It’s all about nurturing the beneficial bacteria and reducing the growth of less desirable ones. This involves a holistic approach that goes beyond just popping a pill.
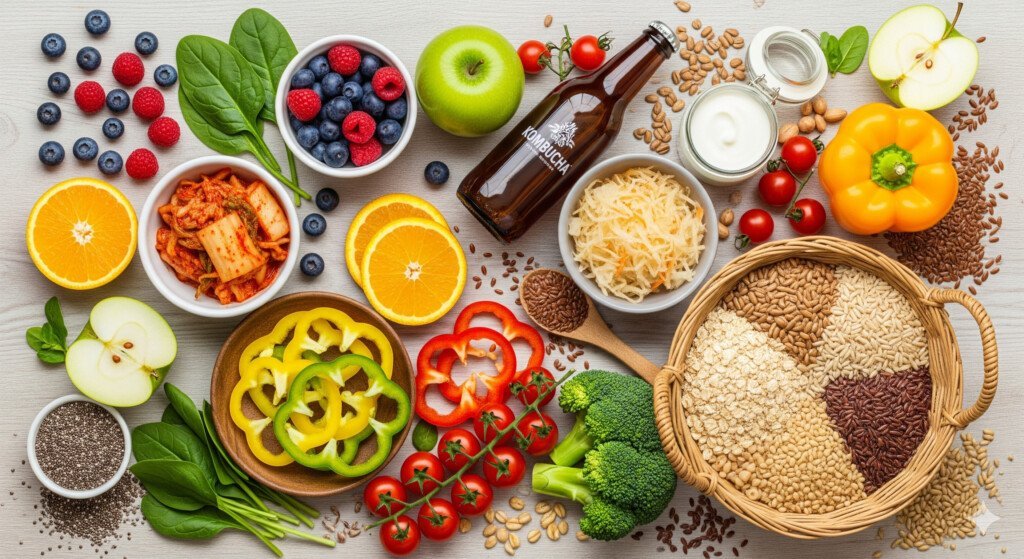
1. Embrace a Diverse, Fiber-Rich Diet: This is the cornerstone of gut health. * Prebiotic Foods: These are non-digestible fibers that feed your beneficial gut bacteria. Think garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, apples, oats, and whole grains. * Resistant Starch: Found in foods like cooled cooked potatoes, green bananas, and legumes, resistant starch acts like fiber, feeding your gut microbes. * Plant Diversity: Aim for a wide variety of plant foods in your diet. Each plant contains different fibers and nutrients that support different beneficial bacterial strains.
2. Incorporate Fermented Foods: These are natural sources of probiotics. * Yogurt and Kefir: Choose plain, unsweetened varieties with live active cultures. * Sauerkraut and Kimchi: Fermented cabbage rich in beneficial bacteria. * Kombucha: A fermented tea beverage. * Tempeh and Miso: Fermented soy products.
3. Reduce Processed Foods, Sugar, and Artificial Sweeteners: These ingredients can disrupt the delicate balance of your gut microbiome, promoting the growth of harmful bacteria and increasing inflammation, counteracting your efforts for gut health and weight loss.
4. Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for the movement of food through your digestive system and for maintaining a healthy gut lining.
5. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact your gut microbiome and gut barrier function. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
6. Get Enough Sleep: Sleep deprivation can alter gut bacteria composition and lead to increased inflammation, hindering your weight loss journey.
7. Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes a more diverse and beneficial gut microbiome, further supporting digestive health and fat burning.

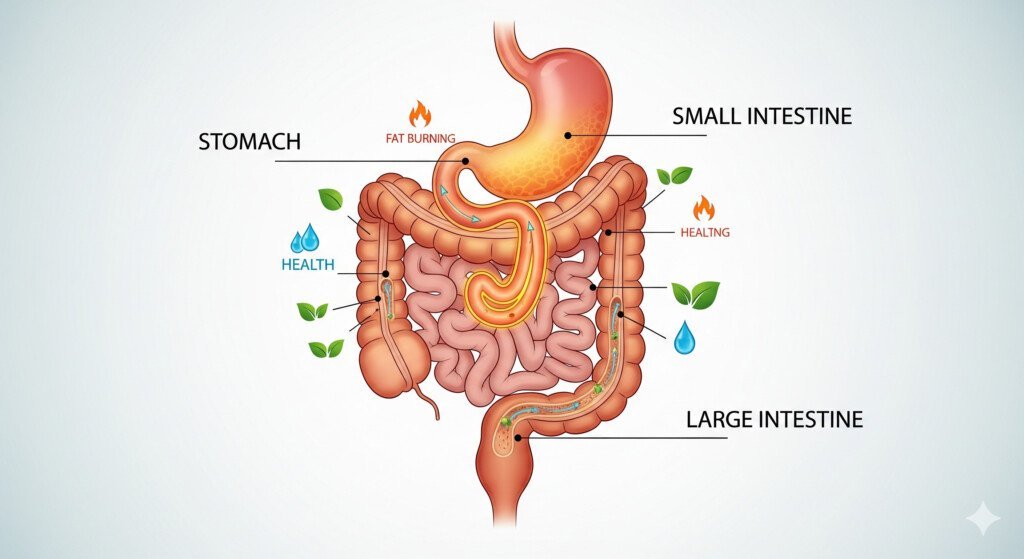
Digestive Health & Fat Burning: Beyond the Basics
Beyond just the bacteria themselves, maintaining overall digestive health for fat burning involves several other factors.
- Stomach Acid (HCl): Adequate stomach acid is crucial for breaking down food, especially protein, and killing off harmful bacteria that might enter your system. Low stomach acid can lead to indigestion and dysbiosis.
- Enzymes: Digestive enzymes, produced by your body (pancreas) and found in some foods, help break down macronutrients into absorbable units. If you struggle with digestion, digestive enzyme supplements can sometimes be helpful, but they should be used under guidance.
- Gut Motility: Regular bowel movements are vital for eliminating waste and toxins. Constipation can contribute to an unhealthy gut environment. Fiber, hydration, and exercise are key.
- Gut Barrier Integrity (“Leaky Gut”): Your gut lining acts as a crucial barrier, allowing nutrients in while keeping toxins and undigested food particles out. When this barrier becomes compromised (often called “leaky gut”), it can lead to systemic inflammation, which is strongly linked to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction. Nutrients like L-glutamine can support gut lining repair.
By addressing these foundational aspects of digestive health, you create an optimal environment for your beneficial gut bacteria to thrive, making your body a more efficient fat-burning machine. This integrated approach to gut health and weight loss is powerful.
The Bottom Line: Cultivating a Healthy Gut for Lasting Weight Loss
The journey to lasting weight loss is rarely simple, but understanding the role of gut health in weight loss adds a crucial dimension to your strategy. Your gut microbiome isn’t just a passenger; it’s an active participant, influencing your metabolism, appetite, inflammation, and overall body composition.
By focusing on nourishing your gut with a diverse, fiber-rich diet, incorporating fermented foods, managing stress, and living an active lifestyle, you empower your body to burn fat more efficiently and maintain a healthy weight. This isn’t a quick fix, but a sustainable path towards a healthier, leaner you, built from the inside out. Embrace the power of your gut, and unlock a new level of well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1: Can specific gut bacteria make me gain weight?
Research suggests that certain bacterial compositions in the gut, particularly a higher ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes, may be more efficient at extracting calories from food and storing them as fat, potentially contributing to weight gain. This highlights the importance of fostering a diverse and balanced microbiome for gut health and weight loss.
2: Are all probiotic supplements good for weight loss?
Not necessarily. The effects of probiotics are highly strain-specific. While some strains, like Lactobacillus gasseri, have shown promise in certain studies for fat reduction, not all probiotics are designed for or proven to aid weight loss. It’s best to look for specific strains or a diverse blend and combine them with a healthy lifestyle.
3: How quickly can I improve my gut health for weight loss?
Changes in your gut microbiome can occur relatively quickly, often within a few days or weeks of dietary changes. However, consistent and sustained effort is required for significant and lasting improvements to your gut health and weight loss journey. Think long-term lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes.
4: What are the best foods to eat for gut health and weight loss?
Focus on a diverse range of whole, unprocessed foods. Key examples include: * Prebiotic-rich foods: Garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, oats. * Fermented foods: Plain yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, tempeh. * Fiber-rich foods: All vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains. These foods nourish beneficial gut bacteria, crucial for digestive health and fat burning.
5: Can stress impact my gut health and weight loss?
Absolutely. The gut-brain axis is a strong connection. Chronic stress can negatively alter your gut microbiome composition, increase gut permeability (“leaky gut”), and contribute to inflammation, all of which can hinder your weight loss efforts and overall gut health and weight loss. Managing stress through mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep is vital.
Disclaimer:
This post may contain affiliate links. If you purchase through them, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Also, this content is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice.